For the most part canker sores, also called recurrent aphthous stomatitis or oral aphthae are a localized condition that may be caused by mild trauma to the mouth, a food allergy or sensitivity, or hormone fluctuations or other unknown causes. There is no one cause and just why some people are prone to canker sores is still being investigated. However, in a small number of cases, the mouth sore is mimicking or a symptom of another condition. It is important to understand if your ulcer has an underlying cause in order to pick to best canker sore treatment. While one of the most serious is oral cancer, we will look at several other possibilities as well.
Autoimmune Conditions
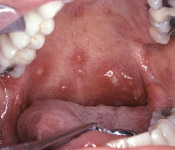 HIV
HIV
Mouth sores are frequently seen in HIV-positive patients due to their compromised immune system. They are not a sign of the disease, so don’t freak out every time you get a canker sore and automatically assume you have AIDS. Oral issues are quite common in people living with HIV, in fact more than a third experience issues such as mouth sores.
Behçet’s Syndrome
Behçet’s syndrome is a chronic condition caused by an inflammation of the blood vessels. It damages the veins and arteries. Sufferers of this disorder often experience frequent sores in the mouth and/or genital area, as well as sores on other parts of their body, joint pain and eye inflammation. If you suffer from sores or lesions in other parts of your body in addition to your mouth, you should see your health professional.
Lupus
Canker sores are associated with lupus patients. Lupus is a chronic autoimmune disorder that can affect many parts of the body including organs, joints and skin. Lupus patients are particularly prone to mouth sores and they tend to be larger, take a longer time to heal and often appear on the roof of the mouth. The appearance of oral aphthae are often associated with flare-up of the disease involving the internal organs. Lupus patients are often treated with systemic corticosteroids to eliminate the mouth sores.
Other immune system disorders that may produce mouth ulcers include myelodysplastic syndromes, and forms of neutropenia. However, these diseases have other symptoms as well.
Viral Infections
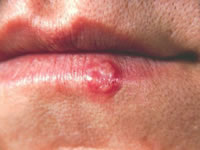
Viral infections including shingles (herpes zoster) and herpes simplex can sometimes imitate canker sores, especially when they involve the lips. An important distinguishing point is that herpes usually affects the outside of the mouth and surrounding area, while canker sores are usually inside the mouth. But there can be some exceptions. On the rare occasion herpes appears on the inside of the mouth it is usually on the lip or gums. Herpes sores are fluid-filled blisters while canker sores are whitish flat lesions that can be very painful.
Gastrointestinal Diseases
Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract have also been associated with recurring aphthous stomatitis. Celiac disease is an intolerance to gluten, which is found in most grains including wheat, barley and rye. By following a gluten-free diet you are usually relieved of symptoms.
Mouth sores can also appear during a flare-up of Crohn’s disease, a condition affective the digestive tract. Ulcerative colitis, a form of inflammatory bowel disease, may also trigger oral ulcers. These diseases of the colon also have many other symptoms.
Vitamin Deficiency
 People with insufficient levels of Vitamins B1, B2, B6, B12, Folic Acid, or Iron have sometimes been diagnosed with recurring canker sores. Your doctor can do a blood test to check your vitamin and mineral levels. It has been found that supplementing with therapeutic levels of vitamins can often resolve the frequent aphthous ulce
People with insufficient levels of Vitamins B1, B2, B6, B12, Folic Acid, or Iron have sometimes been diagnosed with recurring canker sores. Your doctor can do a blood test to check your vitamin and mineral levels. It has been found that supplementing with therapeutic levels of vitamins can often resolve the frequent aphthous ulce
Oral Cancer
Simple aphthous stomatitis heal within about two weeks. Usually the first sign of oral cancer is a mouth lesion that doesn’t heal. Oral cancer can affect the cheek lining, roof of mouth, gums and floor of the mouth. The most common type is squamous cell carcinoma, which can spread rapidly. Tobacco use and heavy alcohol are risk factors.
While most of the time canker sores are nothing to worry about and they usually resolve on their own or can be relieved with a home remedy, sometimes they can be confused with other pathological disorders. If your mouth ulcers have not gone away within a couple of weeks, you should see your doctor to rule out other possible conditions.